What is Diabetes?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the body that regulates glucose and blood glucose, and
Diabetes is a chronic illness resulting either from a short supply of insulin produced by the pancreas, or when produced insulin cannot be effectively used by the body. Demographics with an increased risk for diabetes include those that have a family history of diabetes, obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and smoking.
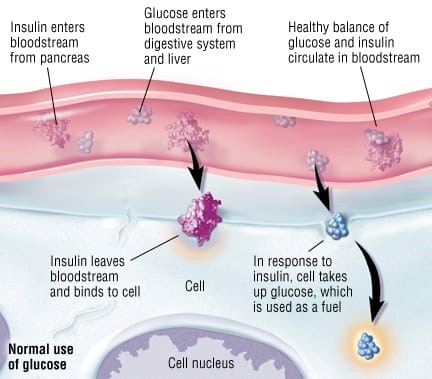
Figure 1 Diabetes Pathophysiology (Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus, n.d.)
Diabetes is classified as a non-communicable disease (NCDs), meaning it is unable to be transmitted from person to person, but it is nonetheless a disease that has been steadily increasing in prevalence and number of cases.
Type 1 vs Type 2 Diabetes
The most prevalent forms of Diabetes can be classified into two major groups: Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.Type 1 diabetes can be described by an autoimmune reaction attacking insulin-producing pancreatic cells. It accounts for nearly 10 percent of all diagnosed diabetic cases, and although in general it is less understood than Type 2 diabetes, it has been researched that autoimmune, environmental, and genetic factors are involved in its development.
Type 2 diabetes can be described by the body being unable to use the insulin it produces, and essentially becoming insulin resistant. This type of diabetes accounts for nearly 95 percent of all diagnosed diabetic cases, and risk factors include obesity, diabetic family histories, older age and physical inactivity. Treatment can be implemented via blood glucose monitoring, diet control, increasing physical activity, insulin or oral medication.
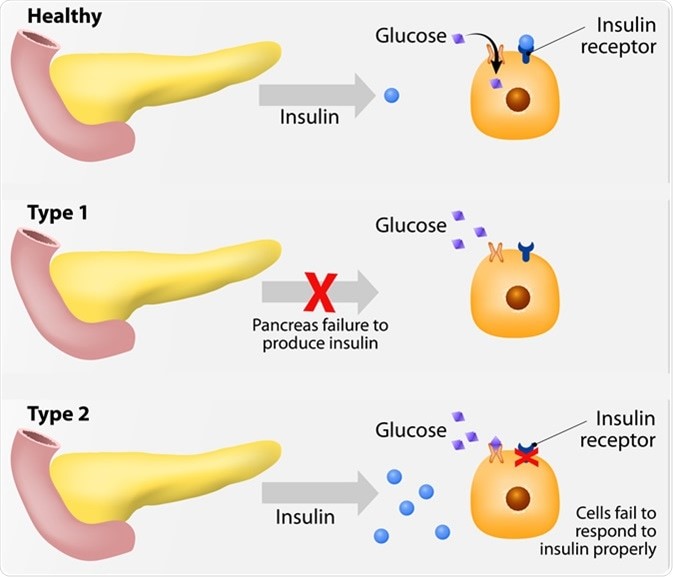
Figure (Diabetes Mellitus Subtypes, 2019)
Complications of diabetic illness
Organ systems in the body are heavily affected by the prevalence of diabetes, meaning individuals suffering from the disease are susceptible to serious health complications. Diabetic complications are classified into microvascular and macrovascular types with the former affecting nervous, renal and ocular systems and the latter affecting cardiovascular, and peripheral vascular diseases.
Early signs and symptoms
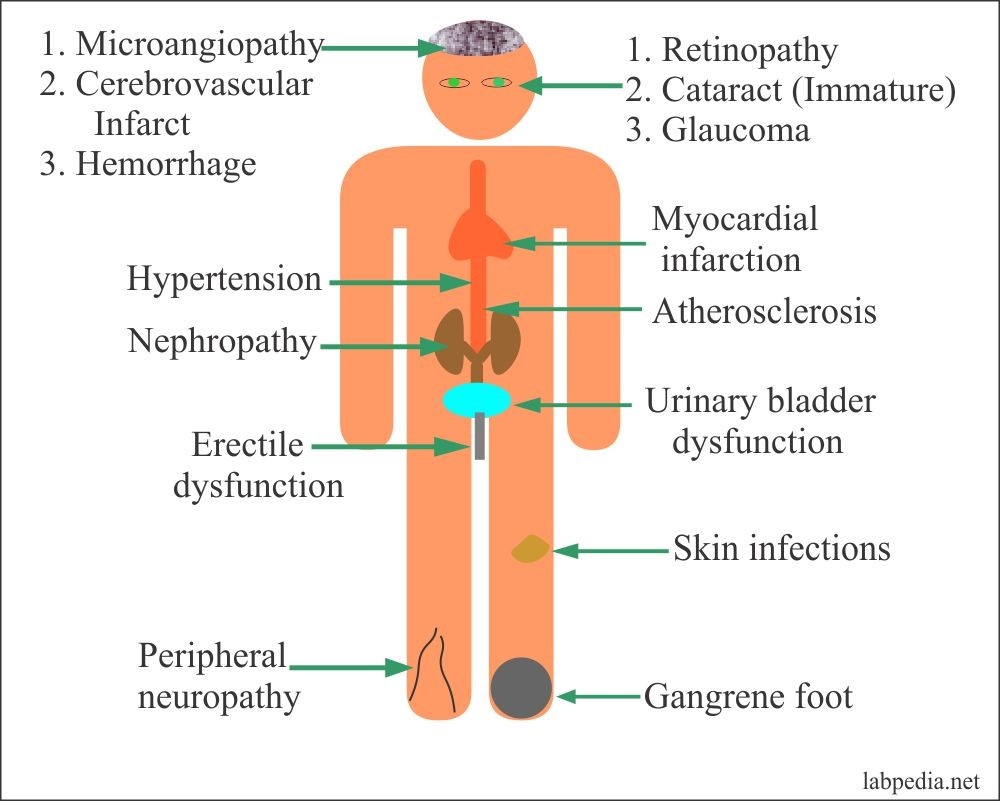
Figure 4 Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes (Spotting Diabetes (Mellitus) Early: Signs and Symptoms |, n.d.)
Diagnosing diabetes at its earliest stages are crucial to getting the disease promptly under control and preventing complications to the vascular system. Unfortunately, damage to the body as a result of the disease can actually start several years prior to the manifestation of signs and symptoms.
Warning signs of diabetes can include persistent fatigue, decreased vision, weight loss, irritability, recurring infections, dry mouth, Acanthoses Nigricans, or even erectile dysfunction to name a few. Described symptoms are characteristic to either one or both of type 1 and type 2 diabetes, depending on the circumstances. For example, unexplained weight loss is common in type 1, but also prevalent in those suffering from undetected type 2 diabetes. These signs and symptoms are essential knowledge to be kept in mind, that when paired alongside medical advice can help identify diabetes in its earlier stages.
References
Alcohol & Diabetes—How They’re Connected, Risks, & More. (n.d.). The Recovery Village
Drug and Alcohol Rehab. Retrieved July 9, 2021, from
https://www.therecoveryvillage.com/alcohol-abuse/faq/alcohol-and-diabetes/
Deshpande, A. D., Harris-Hayes, M., & Schootman, M. (2008). Epidemiology of Diabetes and
Diabetes-Related Complications. Physical Therapy, 88(11), 1254–1264.
https://doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20080020
Diabetes Mellitus Subtypes. (2019, June 27). News-Medical.Net.
https://www.news-medical.net/health/Diabetes-Mellitus-Subtypes.aspx
Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus. (n.d.). Retrieved July 9, 2021, from
https://www.kindredhealthcare.com/resources/blog-kindred-
continuum/2013/11/07/pathophysiology-of-diabetes-mellitus
Roglic, G., & World Health Organization (Eds.). (2016). Global report on diabetes. World
Health Organization.
Spotting Diabetes (Mellitus) Early: Signs and Symptoms |. (n.d.). Retrieved July 9, 2021, from
https://drogunlana.com/2021/02/10/4393/
