What is high blood pressure?
Blood pressure tells us how much force the blood in our blood vessels are pushing with against our vessel walls, and it is symbolized by a reading of systolic over diastolic numbers (I.e. 114/75 mm Hg). The pressure as the heart contracts over the pressure as the heart is resting between contractions. A high blood pressure on the contrary, also known as hypertension, is defined by systolic pressures of values over 140, and any diastolic pressure of values over 90 sustained over long periods of time. If left untreated it may lead to a plethora of both short and long-term health risks including heart attack, heart failure stroke, peripheral arterial disease, or kidney failure.
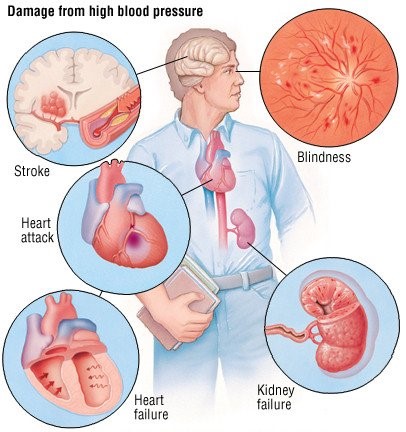
Figure 1. Damage from high blood pressure (High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Guide, n.d.)
What causes high blood pressure?
There is no explicitly identifiable cause or cure for individuals suffering from high blood pressure, but it is a disease that can be diagnosed and managed, and the first step would be to get your blood pressure regularly checked with your physician! In general, as you get older the more prone you are to hypertension. But certain demographics in the population are more susceptible to hypertension than others, including those that share close blood relatives with high blood pressure, and those who are overweight, diabetic, sedentary, consuming too much sodium, alcoholic, or suffering from kidney disease.
What are the signs and symptoms of high blood pressure?
In general, high blood pressure exhibits little to no signs or symptoms, making it a very dangerous health complication if left unnoticed. For starters, getting your blood pressure checked regularly at your physician’s office would be a good practice, in order to sooner identify any signs of irregularity.
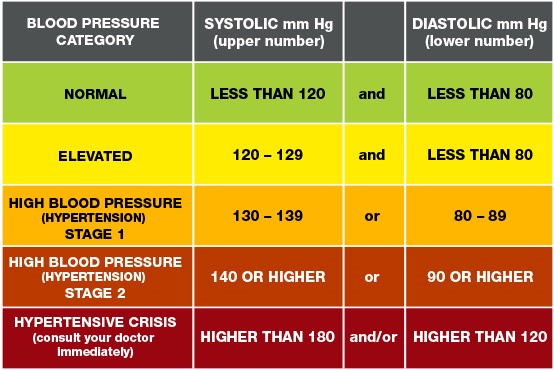
Figure 2. Understanding blood pressure readings (Understanding Blood Pressure Readings, n.d.)
What do I do if I have high blood pressure?
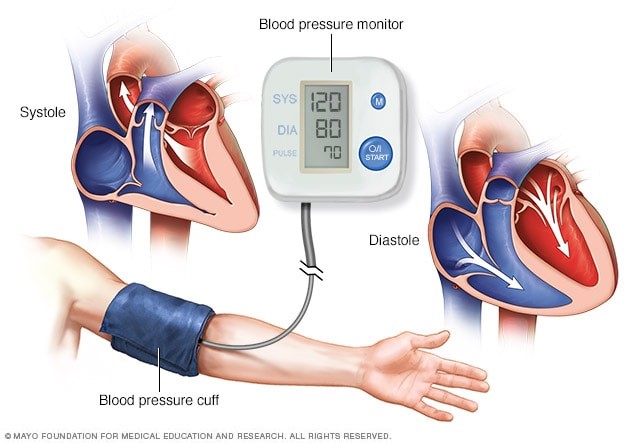
Figure 3. Blood Pressure Measure (Whelton et al., 2018)
Individuals looking to prevent high blood pressure or currently suffering from high blood pressure can look into preventative and maintenance methods to implement into their regular daily lives.
- Learn what your BP should be, and make it a goal to sustain that value
- Reach and maintain a body weight that is healthy
- Increase your levels of physical activity
- Incorporate healthy meals low in sodium, added sugars, and saturated or trans fats you’re your diet
- Alcoholic beverages should be limited in consumption.
Medical intervention?
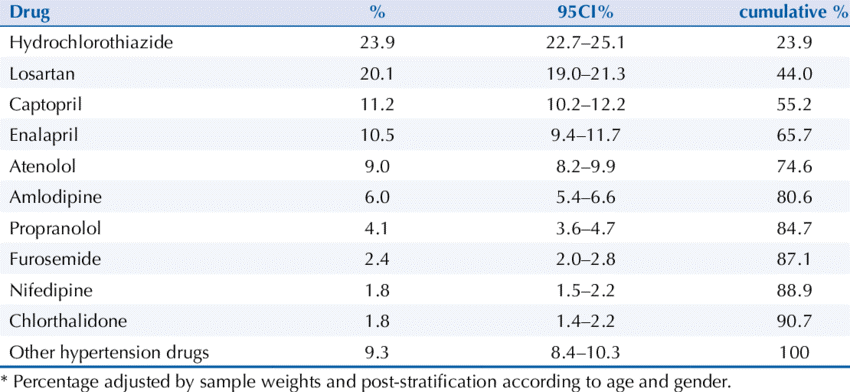
Figure 4. Common drugs used to treat HBP (Most Commonly Used Medicines to Treat High Blood Pressure, Regardless…, n.d.)
On top of the preventative methods listed for those who have high blood pressure, medication is also available— such as vasodilators that help relax and dilate blood vessel for optimal blood flow. Other medications aim to slow down and lower the force with which your heart beats, and diuretics are able to prevent the body from retaining excess salts and water. Speak with your medical health provider in order seek the best treatment method for your body.
References
American Heart Association. (2017). What is high blood pressure? South Carolina State
Documents Depository.
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Guide: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Options. (n.d.).
Drugs.Com. Retrieved July 9, 2021, from https://www.drugs.com/health-guide/high-
blood-pressure-hypertension.html
Most commonly used medicines to treat high blood pressure, regardless… (n.d.). ResearchGate.
Retrieved July 9, 2021, from https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Most-commonly-used-
medicines-to-treat-high-blood-pressure-regardless-of-fixed-dose_tbl1_311568283
Understanding Blood Pressure Readings. (n.d.). Www.Heart.Org. Retrieved July 9, 2021, from
Whelton, P. K., Carey, R. M., Aronow, W. S., Casey, D. E., Collins, K. J., Dennison
Himmelfarb, C., DePalma, S. M., Gidding, S., Jamerson, K. A., Jones, D. W.,
MacLaughlin, E. J., Muntner, P., Ovbiagele, B., Smith, S. C., Spencer, C. C., Stafford, R.
S., Taler, S. J., Thomas, R. J., Williams, K. A., … Wright, J. T. (2018). 2017
ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the
Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: A
Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force
on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension, 71(6).